Golgicide A
CAS No. 1139889-93-2
Golgicide A( —— )
Catalog No. M19453 CAS No. 1139889-93-2
Golgicide A is a potent and rapidly reversible GBF1 inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 51 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 87 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 187 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 357 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 537 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 1188 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameGolgicide A
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionGolgicide A is a potent and rapidly reversible GBF1 inhibitor.
-
DescriptionGolgicide A is a potent highly specific and reversible inhibitor of the cis-Golgi ADP-ribosylation factor guanine nucleotide exchange factors (ArfGEF) GBF1. Golgicide A drastically reduced replication of coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) and other human enterovirus species.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorGBF1
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1139889-93-2
-
Formula Weight284.3
-
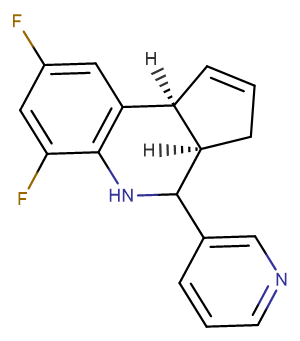
Molecular FormulaC17H14F2N2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:14.2 mg/mL (50 mM)
-
SMILES[H][C@@]12CC=C[C@]1([H])C1=C(NC2C2=CN=CC=C2)C(F)=CC(F)=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Sáenz JB et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2009 5(3) 157-16
molnova catalog



related products
-
HCH6-1
HCH6-1 is a competitive Formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) antagonist.
-
Methyl 3,4,5-trimeth...
Methyl 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamate may protect the heart from arrhythmias via its inhibitory effect on calcium channel.
-
Methyl benzoin
Methyl benzoin is a biochemical.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


